Given an array S of n integers, are there elements a, b, c, and d in S such that a + b + c + d = target? Find all unique quadruplets in the array which gives the sum of target.
Note: The solution set must not contain duplicate quadruplets.
For example, given array S = [1, 0, -1, 0, -2, 2], and target = 0. A solution set is: [ [-1, 0, 0, 1], [-2, -1, 1, 2], [-2, 0, 0, 2] ]
前面有一道3Sum的题,因此手写一气呵成写完,原以为没啥问题,结果第一个testcase都没跑过
package com.maoxiaomeng; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.List; /** * @author lihui * @date 2018/3/26 12:31 */ public class Solution { public List<List<Integer>> fourSum(int[] nums, int target) { List<List<Integer>> tempList = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>(); int len = nums.length; if (nums == null || len < 4) { return tempList; } Arrays.sort(nums); /** * {1, 0, -1, 0, -2, 2}; * {-2, -1, 0, 0, 1, 2}; * i = 0, j = i + 1, left = j + 1, right = len - 1 */ for (int i = 0; i < len - 3; i++) { if (i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1]) { continue; } for (int j = i + 1; j < len - 2; j++) { if (nums[j] == nums[j - 1]) { continue; } int left = j + 1; int right = len - 1; while (left < right) { int sum = nums[i] + nums[j] + nums[left] + nums[right]; if (sum > 0) { right--; } else if (sum < 0) { left++; } else { List<Integer> myList = new ArrayList<Integer>(); myList.add(nums[i]); myList.add(nums[j]); myList.add(nums[left]); myList.add(nums[right]); tempList.add(myList); left++; right--; } while (left < right && nums[left] == nums[left - 1]) { left++; } while (left < right && nums[right] == nums[right - 1]) { right--; } } } } return tempList; } }
居然结果都不对
大半夜的,眼神不好,看了半天也没看出哪里有问题,IDEA设置了个条件断点,i=1,j=2,left=3,right=4这种情况没有输出,看下原因
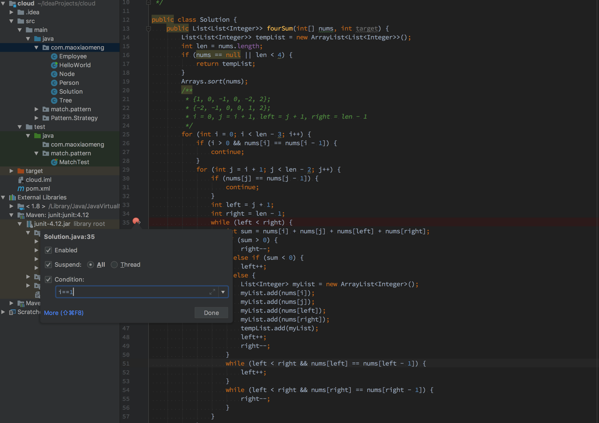
当i=1,j=2,left=3,right=5时,sum>0,right=right-1=4
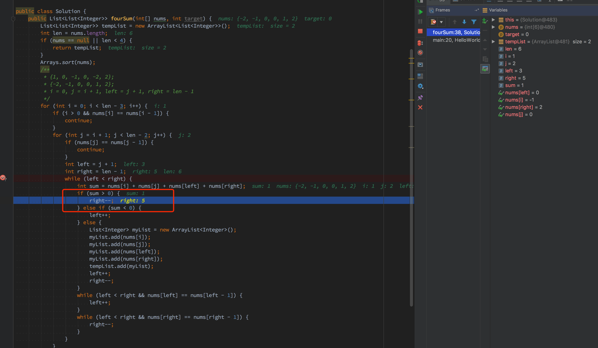
因为right是递减,这就奇怪了,当i=1,j=2,left进到这个判断条件里了,
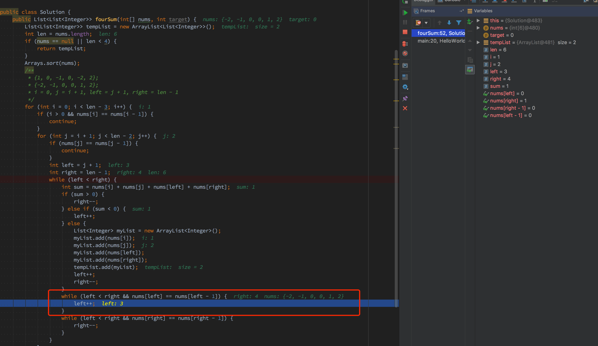
不太对劲,理论上left++了,才会判断是否nums[left] == nums[left-1]避免重复,这里right递减会left++;;仔细一看,最后两个while放错了地方,应该是在else里,避免tempList里重复的myList做的检查
package com.maoxiaomeng; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.List; /** * @author lihui * @date 2018/3/26 12:31 */ public class Solution { public List<List<Integer>> fourSum(int[] nums, int target) { List<List<Integer>> tempList = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>(); int len = nums.length; if (nums == null || len < 4) { return tempList; } Arrays.sort(nums); /** * {1, 0, -1, 0, -2, 2}; * {-2, -1, 0, 0, 1, 2}; * i = 0, j = i + 1, left = j + 1, right = len - 1 */ for (int i = 0; i < len - 3; i++) { if (i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1]) { continue; } for (int j = i + 1; j < len - 2; j++) { if (nums[j] == nums[j - 1]) { continue; } int left = j + 1; int right = len - 1; while (left < right) { int sum = nums[i] + nums[j] + nums[left] + nums[right]; if (sum > 0) { right--; } else if (sum < 0) { left++; } else { List<Integer> myList = new ArrayList<Integer>(); myList.add(nums[i]); myList.add(nums[j]); myList.add(nums[left]); myList.add(nums[right]); tempList.add(myList); left++; right--; while (left < right && nums[left] == nums[left - 1]) { left++; } while (left < right && nums[right] == nums[right - 1]) { right--; } } } } } return tempList; } }
但是结果还是不对,输入[0,0,0,0],返回[]了,应该返回[[0,0,0,0]],原因在第二层for循环,continue的判断多余,这是4个数,不是3个数;3个数只有一个基准,那么nums[i] == nums[i-1]时,已经在上层循环遍历过一次了,此次所以可以跳过;但是4个数有两个基准,nums[i] + nums[j]共同决定,就算nums[i]=nums[j]也不能说明什么;同理else里面的两个while也一样
同样可以调试一把
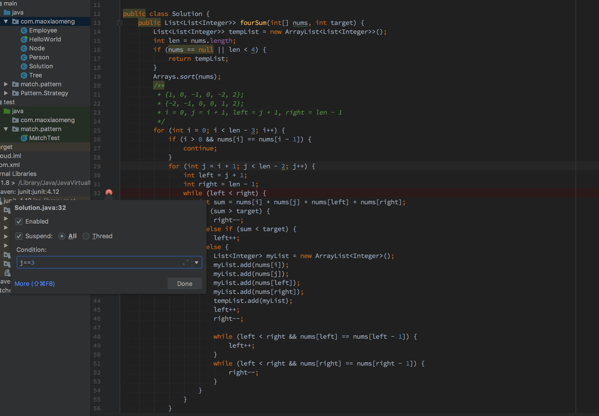
while里做了误操作
解决:
1:去掉j循环体里continue判断
2:else里的while去掉,add的时候加一个判断,myList不重复即可
3:更蛋疼的是,题目要求和为target,而不是0,眼神不好
package com.maoxiaomeng; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.List; /** * @author lihui * @date 2018/3/26 12:31 */ public class Solution { public List<List<Integer>> fourSum(int[] nums, int target) { List<List<Integer>> tempList = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>(); int len = nums.length; if (nums == null || len < 4) { return tempList; } Arrays.sort(nums); /** * {1, 0, -1, 0, -2, 2}; * {-2, -1, 0, 0, 1, 2}; * i = 0, j = i + 1, left = j + 1, right = len - 1 */ for (int i = 0; i < len - 3; i++) { if (i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1]) { continue; } for (int j = i + 1; j < len - 2; j++) { int left = j + 1; int right = len - 1; while (left < right) { int sum = nums[i] + nums[j] + nums[left] + nums[right]; if (sum > target) { right--; } else if (sum < target) { left++; } else { List<Integer> myList = new ArrayList<Integer>(); myList.add(nums[i]); myList.add(nums[j]); myList.add(nums[left]); myList.add(nums[right]); if (! tempList.contains(myList)) { tempList.add(myList); } left++; right--; } } } } return tempList; } }
蛋碎,还觉得很简答
